Phalen Maneuver for Carpal Tunnel: A Key Diagnostic Tool

This article is not medical advice and is not intended to diagnose or treat any diseases or conditions. Please consult with your healthcare provider.
Identifying the source of hand and arm discomfort is paramount, and carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a frequent culprit, marked by symptoms like pain, numbness, and tingling. This condition arises from pressure on the median nerve as it passes through the narrow carpal tunnel in the wrist, often aggravated by activities involving repetitive hand motions.
A precise diagnosis is key to effective management, relying on methods ranging from clinical assessments like the Phalen Maneuver to imaging studies such as diagnostic ultrasound. This article will delve into the specifics of the Phalen Maneuver, assess its utility and constraints, and show how it contributes alongside tools like ultrasound to a comprehensive CTS diagnostic strategy.
Introduction to Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
CTS develops when excess pressure around the median nerve in the wrist leads to symptoms such as tingling, numbness, and pain, and in some instances muscle weakness. The exact cause can vary, ranging from repetitive strain to anatomical predispositions. Because severity differs among individuals, healthcare providers often rely on multiple tools during diagnosis:
- Physical Tests: Simple maneuvers can reveal potential nerve compression.
- Imaging Studies: Diagnostic ultrasound provides real-time images of the tissues and nerves within the wrist.
- Nerve Function Tests: Studies such as nerve conduction tests measure the speed at which electrical signals traverse the nerve.
Each assessment tool contributes important pieces of information that, when taken together, may create a thorough understanding of CTS.
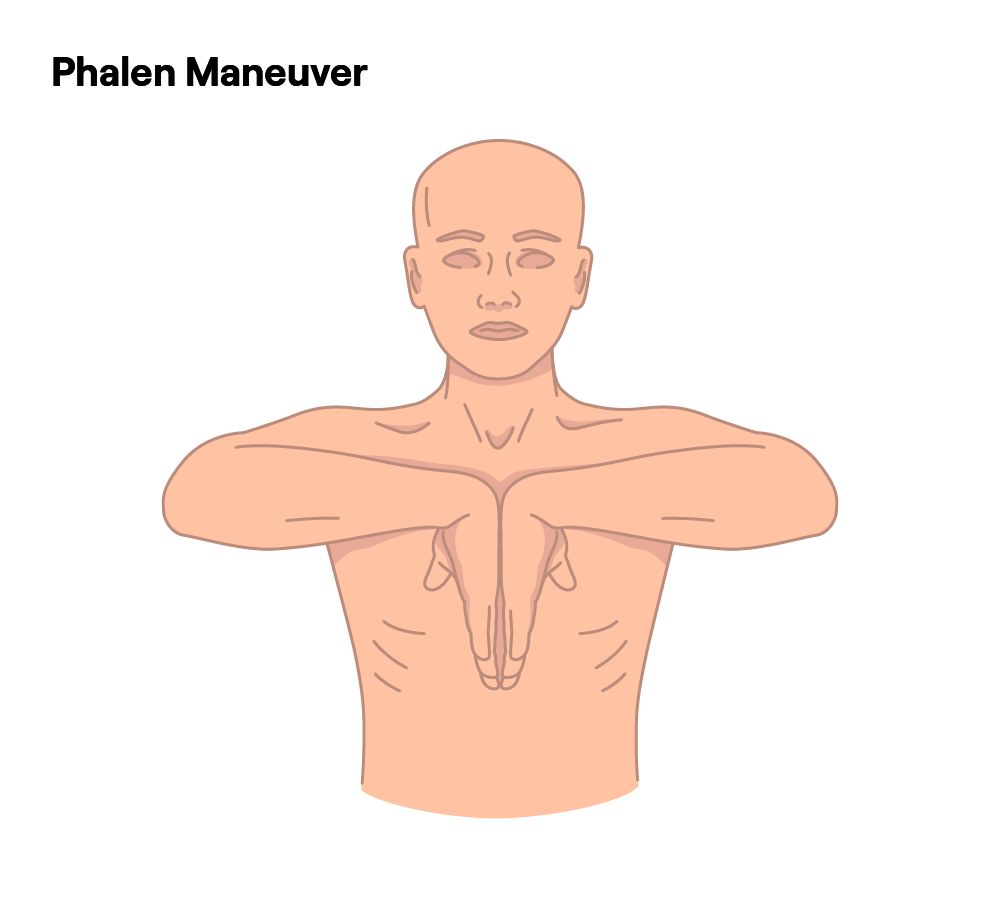
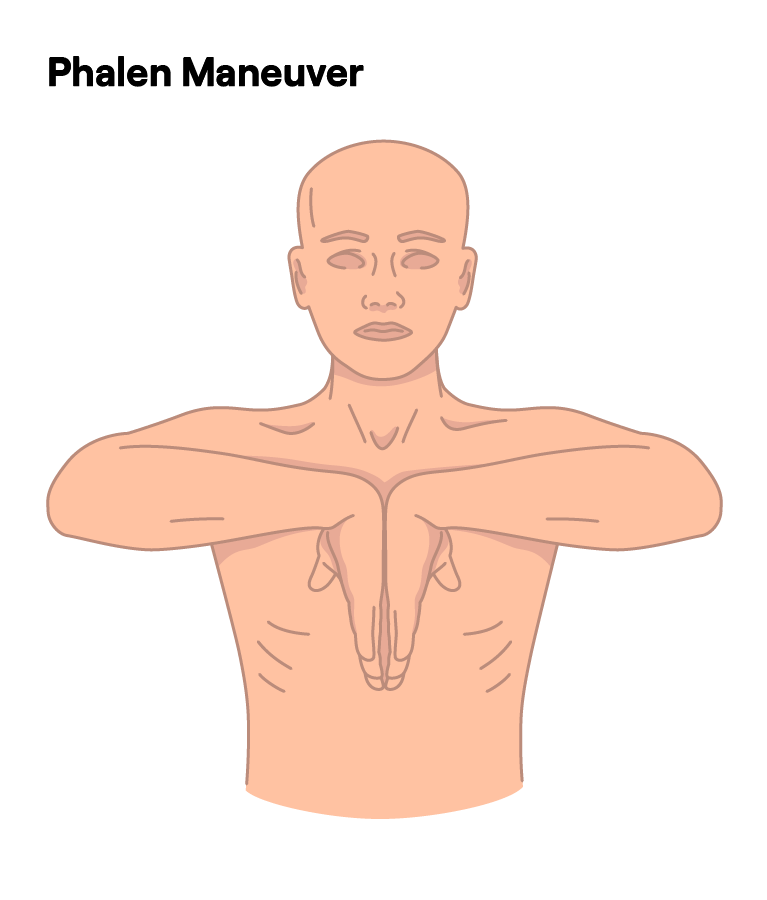
What Is the Phalen Maneuver for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The Phalen Maneuver is a straightforward clinical test used to screen for carpal tunnel syndrome. By positioning the wrists in a way that may reproduce CTS-related symptoms, providers gain insight into whether nerve compression is present.
How to Perform the Phalen Maneuver
This is not intended as a diagnosis. If you think any of this may apply to you, please speak to your healthcare provider.
- Sit in a comfortable position with your forearms supported on a flat surface.
- Relax your shoulders and arms.
- Bend your wrists forward at a 90-degree angle.
- Press the backs of your hands together so the wrists remain flexed.
- Maintain this position for approximately one minute, monitoring any changes in sensation.
If tingling, numbness, or a pins-and-needles feeling arises in the thumb, index, middle, or part of the ring finger, it may indicate a positive test, suggesting possible CTS.
Key Points and Limitations
Benefits
- Straightforward and cost-efficient.
- Requires no special equipment.
- May serve as an initial indicator of CTS.
Limitations
- Other conditions (e.g., arthritis or tendonitis) may produce similar sensations, raising the possibility of false positives.
- Mild cases might not trigger a positive result, leading to false negatives.
- The maneuver alone does not visualize internal structures of the wrist.
Because of these limitations, a Phalen Maneuver is often followed by additional diagnostic methods to confirm or rule out CTS.
Phalen Maneuver Interpretation and Clinical Follow-Up
A positive Phalen Maneuver result may not guarantee a diagnosis of CTS, but it can raise a strong suspicion. Conversely, negative outcomes are not definitive proof of absence. For mild or borderline cases, providers often suggest re-evaluations. If symptoms persist or fluctuate, repeated testing—potentially with additional imaging—helps track changes over time.
Benefits of Early Detection
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Splinting and rest can sometimes decrease symptoms at an early stage.
- Ergonomics: Making changes to a workstation or daily routines helps reduce ongoing stress to the wrist.
- Close Monitoring: Periodic follow-ups allow for swift intervention if CTS worsens.
This balanced approach means that a person with suspected CTS can try conservative measures before considering more direct interventions.
Diagnostic Ultrasound for CTS
Diagnostic ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of anatomical structures. For CTS, this can provide a more direct view of the median nerve and surrounding tissues.
How Diagnostic Ultrasound Works
During an ultrasound evaluation for CTS, a healthcare provider uses a handheld device (transducer) to scan the wrist area. Images appear on the screen simultaneously with the scanning, revealing:
- Median Nerve Appearance: Changes in size or shape of the nerve, helping to detect any swelling.
- Surrounding Tissues: Inflammation, thickening, or other abnormalities that might not be apparent during a standard physical exam.
- Structural Details: Anatomical nuances, such as cysts or tissue variations, that may contribute to nerve compression.
Because this imaging occurs in real time, providers can adjust the transducer’s position instantly to view different angles, improving the accuracy of the evaluation.
Advantages of Diagnostic Ultrasound1
- Immediate Visualization: Providers can see tissue structures on the screen as they move the transducer.
- Painless and Efficient: Ultrasound involves no radiation and minimal discomfort, making it patient-friendly.
- Enhanced Accuracy: A better look at the median nerve may increase diagnostic confidence and reduce uncertainty.
By clarifying questionable cases and providing visual proof of nerve compression, ultrasound can complement the Phalen Maneuver and other clinical tests.
Other Diagnostic Methods for CTS
In addition to the Phalen Maneuver and ultrasound, other tests often factor into CTS diagnosis:
- Tinel’s Sign: A clinician lightly taps over the median nerve to see if that provokes tingling in the fingers. Learn more about Tinel’s Sign.
- Electromyography (EMG): EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles, highlighting effects of prolonged nerve compression.
When these tests are used together, each provides unique data that may explain symptom origins and guide planning for next steps.
Combining Diagnostic Tools for Best Results
While the Phalen Maneuver provides a simple starting point, conclusive diagnosis often relies on multiple evaluations:
- Physical Testing: A positive Phalen Maneuver alerts healthcare professionals to likely median nerve compression.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Offers a detailed look at the wrist, clarifying findings from physical tests.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: Provide objective measurements of how quickly the nerve transmits signals.
Employing each method strategically makes it possible to build a solid, evidence-based diagnosis of CTS.
Selecting the Right Diagnostic Approach for CTS
Determining the most appropriate next step depends on multiple factors, such as symptom severity, duration, and overall health. Physicians typically evaluate patient history and conduct initial exams before recommending advanced diagnostic tools. Those with mild indications might need only a Phalen Maneuver or Tinel’s Sign, while individuals with more persistent or escalating symptoms often benefit from ultrasound and nerve conduction studies.
In some cases, occupational or recreational activities may play a pivotal role in the onset of CTS. Engaging in an open dialogue about the type, frequency, and intensity of manual tasks can help providers pinpoint the underlying cause. Such comprehensive assessments help ensure that the best combination of diagnostic tests—and potentially treatments—are chosen to address each unique situation.
Additional Insights on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
CTS can be influenced by numerous lifestyle and health factors. While laboratory tests are not always central to diagnosis, these factors may also guide medical decisions:
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy, for example, may increase fluid retention and exacerbate wrist swelling, upping the likelihood of CTS.
- Repetitive Tasks: Frequent typing, assembly work, or similar repetitive activities can increase strain on the median nerve.
- Joint or Bone Conditions: Pre-existing wrist or joint problems, such as fractures or arthritis, can add pressure in the carpal tunnel area.
Healthcare providers generally discuss these considerations when deciding which diagnostic approach is most suitable. Recognizing risk factors tends to sharpen the overall clinical picture, allowing for more targeted strategies in both diagnosis and management.
Take a CTS Assessment

Emerging Trends in Carpal Tunnel Diagnostics
Technological progress has broadened how healthcare professionals approach CTS diagnosis:
- Portable Ultrasound: Smaller, more affordable devices allow providers to perform real-time imaging in various clinical settings or areas with limited resources.
- Refined Ultrasound Techniques: Imaging procedures continue to be refined, potentially increasing the accuracy of early CTS detection.
- Integrated Data Analysis: Combining different test results in specialized software could provide faster interpretation and guide precise treatment plans.
These advances underscore the evolving nature of CTS diagnostics, encouraging clinicians to seek continuous improvement for patient care.
After Diagnosis: Navigating Carpal Tunnel Management Options
Once a diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome is confirmed through methods like the Phalen Maneuver, clinical examination, and potentially diagnostic ultrasound, the focus shifts to management. The goal is to alleviate symptoms, improve hand function, and prevent further nerve compression. Treatment strategies range from conservative measures to more definitive procedures, depending on the severity and persistence of your CTS.
Initial and Conservative Approaches
For many individuals, especially those with mild to moderate symptoms, conservative management strategies are the first line of defense. These approaches aim to reduce pressure on the median nerve and manage symptoms without surgical intervention:
- Splinting and Ergonomics: Wearing a wrist splint, particularly at night, can help maintain the wrist in a neutral position, reducing pressure on the nerve. Ergonomic adjustments to your workstation or daily tasks—such as optimizing keyboard height, using an ergonomic mouse, or modifying tool grips—can also significantly decrease strain on the wrist.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can guide you through specific exercises designed to improve wrist and hand mobility, strengthen supporting muscles, and promote better nerve gliding. They may also employ other modalities to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Identifying and modifying repetitive activities that exacerbate symptoms is crucial. This might involve taking more frequent breaks, altering techniques for certain tasks, or avoiding prolonged wrist flexion/extension.
When Conservative Measures Aren’t Enough: Carpal Tunnel Release with Ultrasound Guidance (CTR-US)
If symptoms persist or worsen despite a thorough trial of conservative treatments, or if CTS is severe at diagnosis, more definitive interventions may be recommended. Carpal tunnel release with ultrasound guidance (CTR-US) is an advanced, minimally invasive procedure that offers effective relief. This technique is specifically designed to alleviate pressure on the median nerve by precisely releasing the transverse carpal ligament, the structure that forms the “roof” of the carpal tunnel.
How CTR-US Works
CTR-US represents a significant advancement in treating carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Minimally Invasive: The procedure is performed through a small incision, which can lead to less post-procedural discomfort and minimal visible scarring compared to traditional open surgery.2-5
- Ultrasound-Guided Precision: Real-time ultrasound guidance is used throughout the procedure. This allows the physician to visualize the median nerve, surrounding blood vessels, and the transverse carpal ligament with clarity, ensuring accurate release of the ligament while protecting vital structures.
- Clinic-Based Convenience: CTR-US is typically performed in a clinic setting under local anesthesia, meaning you can go home shortly after the procedure.2,3,6,7
- Targeted Relief: It is specifically recommended for individuals whose CTS symptoms have not resolved with nonsurgical methods, offering a direct approach to decompressing the median nerve.
Please speak to your healthcare professional to discuss the risks and benefits of CTR-US.
The use of ultrasound guidance enhances the safety and efficacy of the carpal tunnel release, allowing for a targeted approach to address the underlying cause of compression.
The Importance of Ongoing Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regardless of the chosen treatment path, managing carpal tunnel syndrome is an ongoing process. Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider is important:
- Tracking Progress: Monitoring allows for assessment of treatment effectiveness and any changes in symptoms.
- Adjusting Strategies: If CTS is related to occupational factors or other health conditions (like those mentioned in “Additional Insights on Carpal Tunnel Syndrome” above), ongoing adjustments to ergonomics or management of underlying conditions may be necessary.
- Long-Term Well-being: Consistent follow-up helps ensure that you maintain the best possible hand function and quality of life, with prompt intervention if symptoms recur or new issues arise.
Get a Free Screening
Millions of people delay carpal tunnel treatment until their symptoms become unbearable. Don’t wait—sign up for a free screening today to learn if your symptoms may be related to CTS.

Wrapping Up: The Role of the Phalen Maneuver in Comprehensive Carpal Tunnel Assessment
The Phalen Maneuver for carpal tunnel is a useful starting point in identifying signs of median nerve compression. However, it has limitations, and symptoms may not always present clearly during this brief test. That is why diagnostic ultrasound, which provides a dynamic view of internal wrist structures, can be an important addition to one’s diagnostic strategy.
If you find that numbness, tingling, or hand weakness is affecting your normal routine, consider reaching out for a thorough assessment. Schedule an evaluation to discuss your symptoms and learn how one or more diagnostic tests might guide you toward the right course of action for addressing CTS.
MP04209rA
Each person’s experiences, risks, and outcomes may vary. The information provided Carpal tunnel release under real-time ultrasound guidance using UltraGuideCTR™ is intended to transect the transverse carpal ligament for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Many patients benefit from this technique, but results may vary. Talk to your doctor to see if this treatment option is right for you. For full safety information, please visit our Instructions for Use and Safety Information Page.
References:
- Miller LE, Hammert WC, Rekant MS, Fowler JR. Diagnostic accuracy of neuromuscular ultrasound vs. electrodiagnostic studies for carpal tunnel syndrome: systematic review and meta-analysis of paired accuracy studies. Hand (N Y). 2024 Sep 26:15589447241278972. doi: 10.1177/15589447241278972.
- Eberlin KR, Amis BP, et al. Multicenter randomized trial of carpal tunnel release with ultrasound guidance versus mini-open technique. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2023;20(7):597-605. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2023.2218548.
- Pistorio AL, Marwin VM, Paterson PD, Alexander RD, Nelson JT, Miller LM. Office-Based Carpal Tunnel Release with Ultrasound Guidance: 6-month Outcomes from the Multicenter ROBUST Trial. J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsg.2023.12.005.
- Aguila D, Kirsch M, Kindle B, Paterson P. Long-Term Clinical Results of Carpal Tunnel Release Using Ultrasound Guidance: A Multicenter Pragmatic Study. J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2023;6(1):79-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsg.2023.10.001.
- Eberlin KR, Amis BP, et al. Final 1-year results of the TUTOR randomized trial comparing carpal tunnel release with ultrasound guidance to mini-open technique. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024;12(3):e5665.
- Fowler JR, Chung KC, Miller LE. Multicenter pragmatic study of carpal tunnel release with ultrasound guidance. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2022;19(3):273-280. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2022.2048816.
- Bergum RA, Ciota MR. Office-Based Carpal Tunnel Release Using Ultrasound Guidance in a Community Setting: Long-Term Results. Cureus. 2022;14(7): e27169. doi: 10.7759/cureus.27169


